Hubble Jewels
This page is abandoned for the time being.
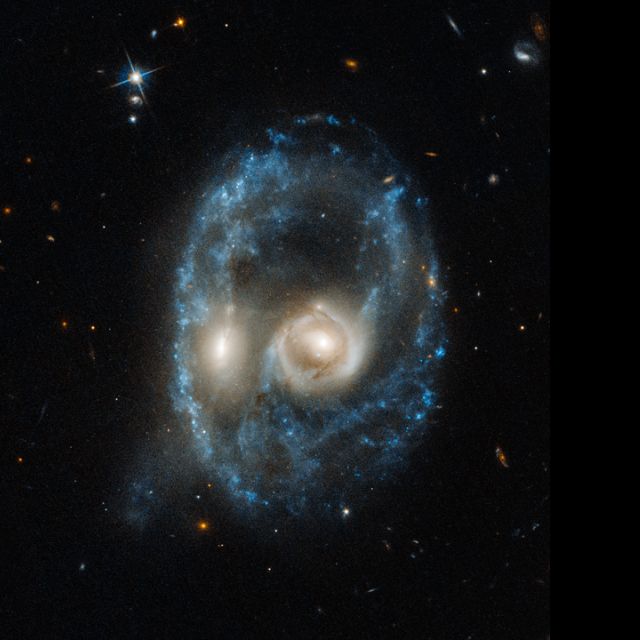
Pair of Interacting Galaxies
2019-11-05
Each "nucleus" is the bright core of a galaxy, one of which slammed into another. The outline of the face is a ring of young blue stars. Other clumps of new stars form a nose and mouth. The violent encounter gives the system an arresting "ring" structure for only a short amount of time, about 100 million years. Ring galaxies are rare; only a few hundred of them reside in our larger cosmic neighborhood. The galaxies have to collide at just the right orientation to create the ring. The galaxies will merge completely in about 1 to 2 billion years, hiding their messy past. Image is about 1.3 arcmin across.
Object: Arp-Madore 2026-424
Constellation: Grus
Distance: 704,000,000 ly
Star Chart | DSS IR Image 🔗
Image credit: NASA, ESA, and J. Dalcanton, B.F. Williams, and M. Durbin (University of Washington)
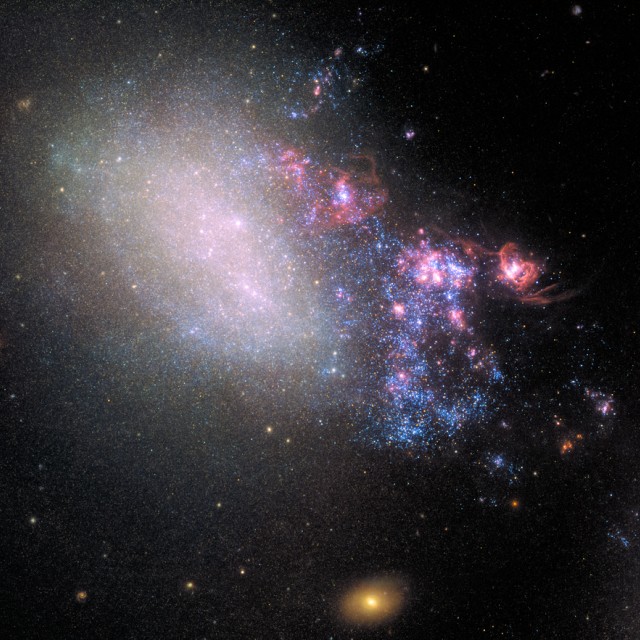
Encounter of Galaxies
2019-05-17
The irregular galaxy NGC 4485 shows all the signs of interaction with a bypassing galaxy without destroying and spawning a new generation of stars, and presumably planets. The right side of the galaxy is ablaze with star formation, shown in the plethora of young blue stars and star-incubating pinkish nebulae. The left side looks intact. It contains hints of the galaxy's previous spiral structure, which was undergoing normal galactic evolution. The larger culprit galaxy off the bottom of the frame is NGC 4490, 24,000 light-years apart.
Object: NGC 4485
Constellation: Canes Venatici
Distance: 25,000,000 ly
Magnitude: 12
Star Chart | DSS IR Image 🔗
Image credit: NASA and ESA; Acknowledgment: T. Roberts (Durham University, UK), D. Calzetti (University of Massachusetts) and the LEGUS Team, R. Tully (University of Hawaii), and R. Chandar (University of Toledo)
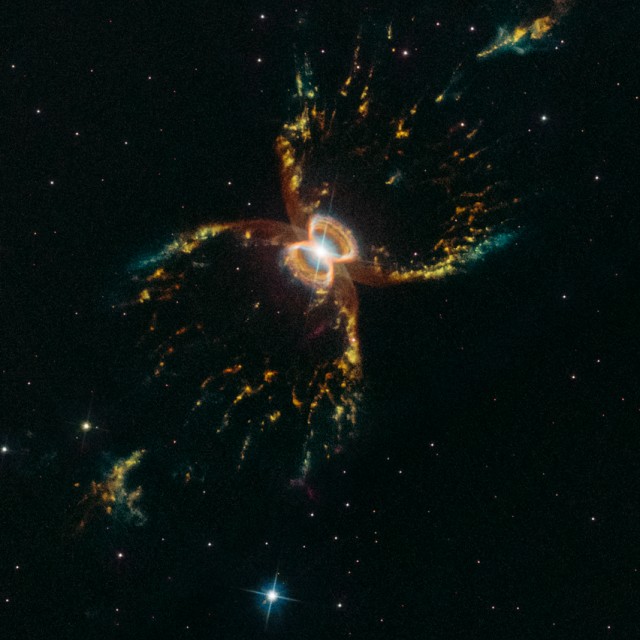
Southern Crab Nebula
2019-04-19
He2-104 is a nebula with a symbiotic Mira variable and white dwarf pair about 1.4 arcmin or 4.4 light-years wide. It appears to have two nested hourglass-shaped structures that were sculpted by a whirling pair of stars in a binary system. The duo consists of an aging red giant star and a burned-out star, a white dwarf. The red giant is shedding its outer layers. Some of this ejected material is attracted by the gravity of the companion white dwarf.
Object: He2-104
Constellation: Centaurus
Distance: 10,700 ly
Magnitude: 6.7
Star Chart | DSS IR Image 🔗
Image credit: NASA, ESA, and STScI
Cosmic Ducks
2019-03-30
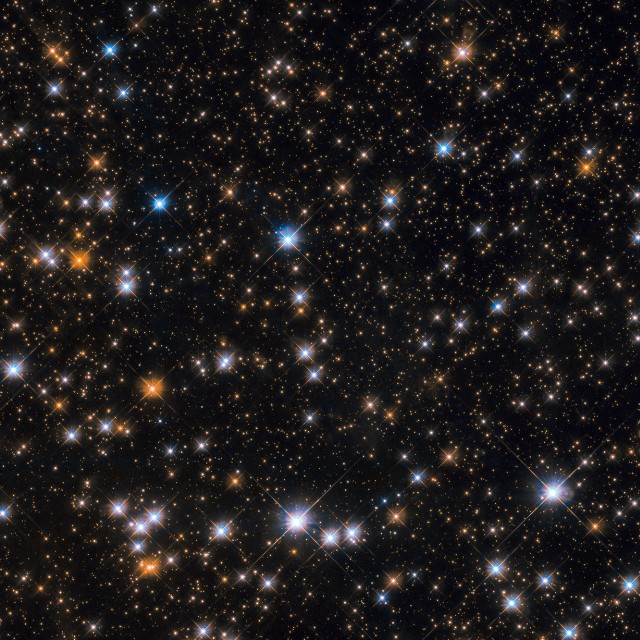
This star-studded image shows us a portion of Messier 11, an open star cluster in the southern constellation of Scutum (the Shield) which is also known as the "Wild Duck Cluster", as its brightest stars form a “V” shape that somewhat resembles a flock of ducks in flight. Messier 11 is one of the richest and most compact and densely populated open clusters currently known. Of the 26 open clusters included in the Messier catalog, M11 is the most distant that can be seen with the naked eye. Containing over 2900 stars, it appears as a triangular patch of light through a pair of binoculars.
Object: Messier 11
Constellation: Scutum
Distance: 6,200 ly
Magnitude: 5.8
Star Chart | DSS IR Image 🔗
Image credit: ESA/Hubble & NASA, P. Dobbie et al.
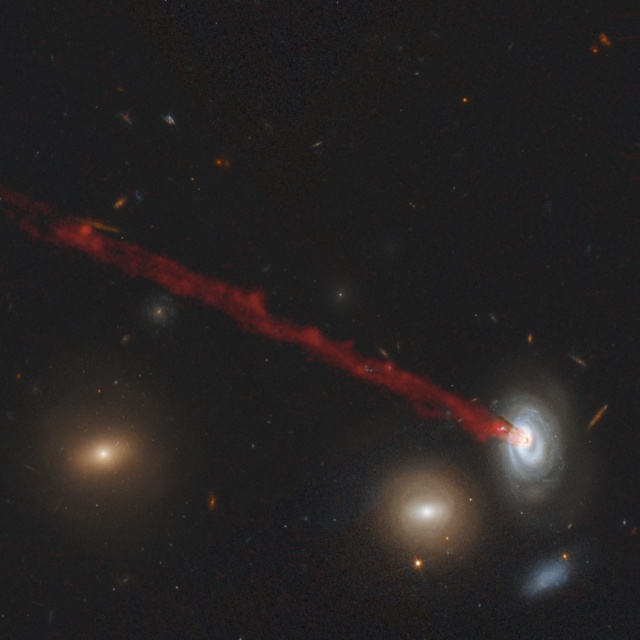
Coma Galaxy D100
2019-01-25
The spiral galaxy D100 is being stripped of its gas as it plunges toward the center of the giant Coma galaxy cluster. The dark brown streaks near D100's central region are silhouettes of dust escaping from the galaxy. The extended gas tail, fueled by the ongoing loss of hydrogen gas from D100, is about 200,000 light-years long, contains about 400,000 times the mass of our Sun, and stars are forming within it. The telescope's sharp vision also uncovered the blue glow of clumps of young stars in the tail.
Object: Galaxy D100
Constellation: Coma Berenices
Distance: 336,000,000 ly
Star Chart | DSS IR Image 🔗
Image credit: NASAESAHubbleSubaru TelescopeW. CramerYaleet al.M. YagiJ. DePasquale
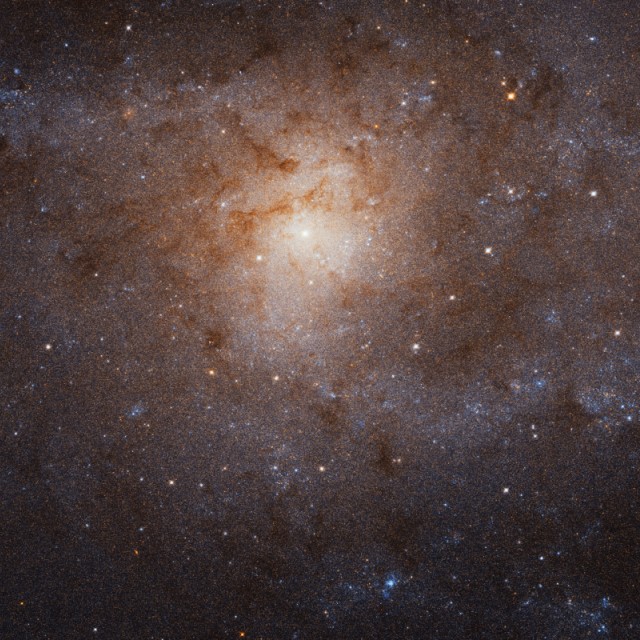
Triangulum Galaxy
2019-01-08
This Hubble image resolves some 25 million stars in this naked-eye spiral galaxy about 60,000 light-years across, which is roughly 40% the size of the Milky Way, and an apparent size of 70.8 × 41.7 arc min. M33 is one of our neighbors in a collection of dozens of galaxies called the Local Group.
Object: Messier 33
Constellation: Triangulum
Distance: 3,000,000 ly
Magnitude: 5.72
Star Chart | DSS IR Image 🔗
Image credit: NASA, ESA, and M. Durbin, J. Dalcanton, and B.F. Williams (University of Washington)
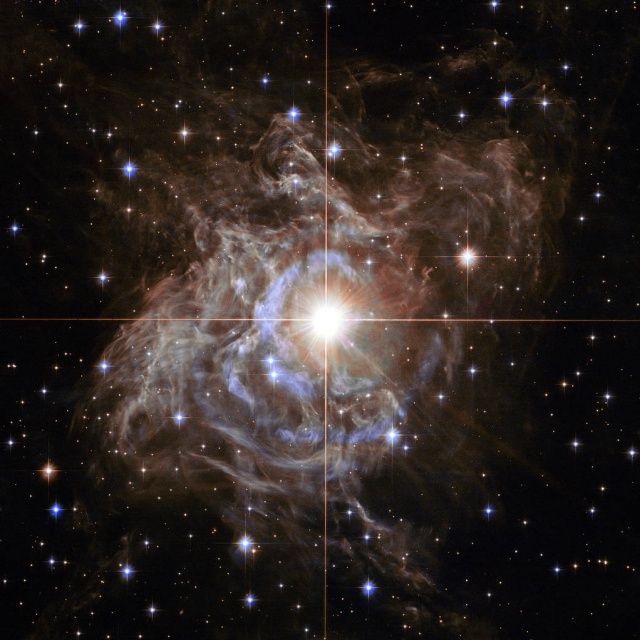
Cosmic Holiday Wreath
2018-12-22
About 10 times more massive and 200 times larger than the sun, Cepheid variable RS Puppis outshines the sun over 20,000 times. The giant star rhythmically brightens and dims over a 41.5 days (varying radius, temperature, and luminosity) cycle (6.52 to 7.67 magnitudes) while the nebula flickers in brightness as pulses of light from the Cepheid propagate outwards. Its spectral type varies between F9 and G7 as its temperature changes.
Object: RS Puppis
Constellation: Puppis
Distance: 6,500 ly
Magnitude: 6.5
Star Chart | DSS IR Image 🔗
Image credit: NASA, ESA and the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA) – Hubble/Europe Collaboration; Acknowledgement: H. Bond (STScI and Pennsylvania State University)
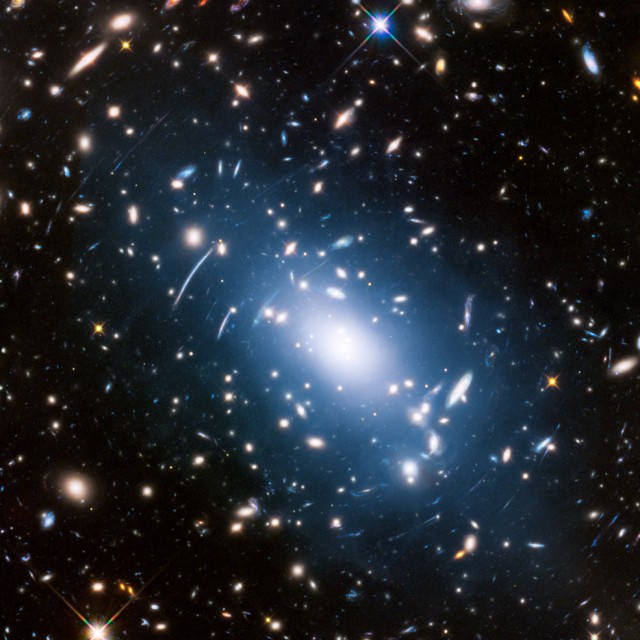
Dark Matter Illuminated
2018-12-21
Hubble captures a soft blue haze, called intracluster light, among innumerable galaxies in the Abell S1063 cluster. The stars producing this glow have been thrown out from their galaxies. These stars now live solitary lives, no longer part of a galaxy but aligning themselves with the gravity of the overall cluster. Astronomers have found that intracluster light's association with a map of mass distribution in the cluster's overall gravitational field makes it a good indicator of how invisible dark matter is distributed in the cluster.
Object: Abell S1063
Constellation: Grus
Star Chart | DSS IR Image 🔗
Image credit: NASA, ESA and M. Montes (University of New South Wales)
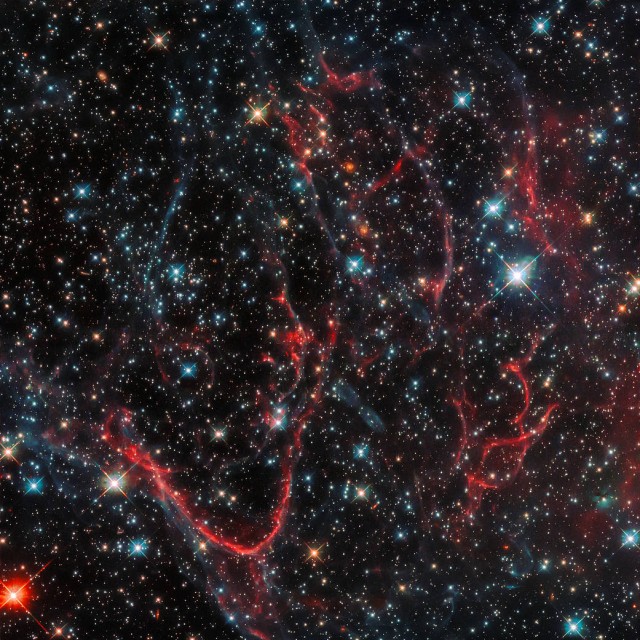
Supernova Remnants
2018-11-30
SNR 0454-67.2 is a supernova remnant, created after a massive star ended its life in a cataclysmic explosion and threw its constituent material out into surrounding space. This created the messy formation we see in this NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope image, with threads of red snaking amidst dark, turbulent clouds. SNR 0454-67.2 is situated in the Large Magellanic Cloud. The remnant is likely the result of a Type Ia supernova explosion; this category of supernovae is formed from the death of a white dwarf star. The image spans about 2 arc second.
Object: SNR+0454-67.2
Constellation: Dorado
Distance: 163,000 ly
Star Chart | DSS IR Image 🔗
Image credit: ESA / Hubble, NASA
Stars Across Generations
2018-11-24
NGC 1866 is located at the edge of the Large Magellanic Cloud. Spanning over 5.5 arc minutes, it is a young globular cluster gathering several generations of chemically homogeneous stars.
Object: NGC 1866
Constellation: Dorado
Distance: 160,000 ly
Magnitude: 9.73
Star Chart | DSS IR Image 🔗
Image credit: ESA/Hubble & NASA
Ghost of Cassiopeia
2018-10-25
The IC 63 nebula is associated with the extremely luminous star Gamma Cassiopeiae, which unleashes as much energy as 34,000 suns. The Ghost Nebula is part of a much larger nebulous region surrounding γ Cassiopeiae that measures approximately two degrees on the sky. IC 63 itself spans over 10 arc minutes.
Object: IC 63
Constellation: Cassiopeia
Distance: 550 ly
Magnitude: 13.33
Star Chart | DSS IR Image 🔗
Image credit: NASA, ESA and STScI; Acknowledgment: H. Arab (University of Strasbourg)
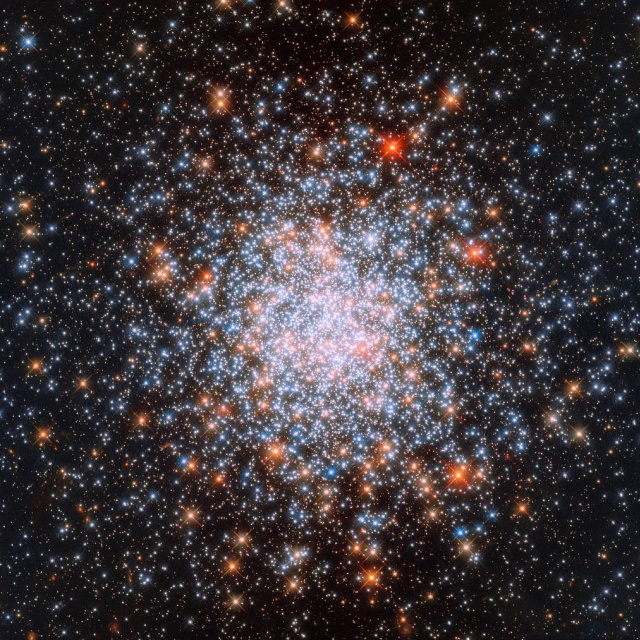
Star Cluster in Nearby Galaxy
2018-10-19
The globular cluster NGC 1898 lies toward the center of the Large Magellanic Cloud.
Object: NGC 1898
Constellation: Dorado
Distance: 170,000 ly
Magnitude: 11.86
Star Chart | DSS IR Image 🔗
Image credit: ESA/Hubble & NASA