Astronomical database with 3D simulations, visualizations, computations, review, articles, and more.
This website is not tailored to smartphones or other hand-held devices.

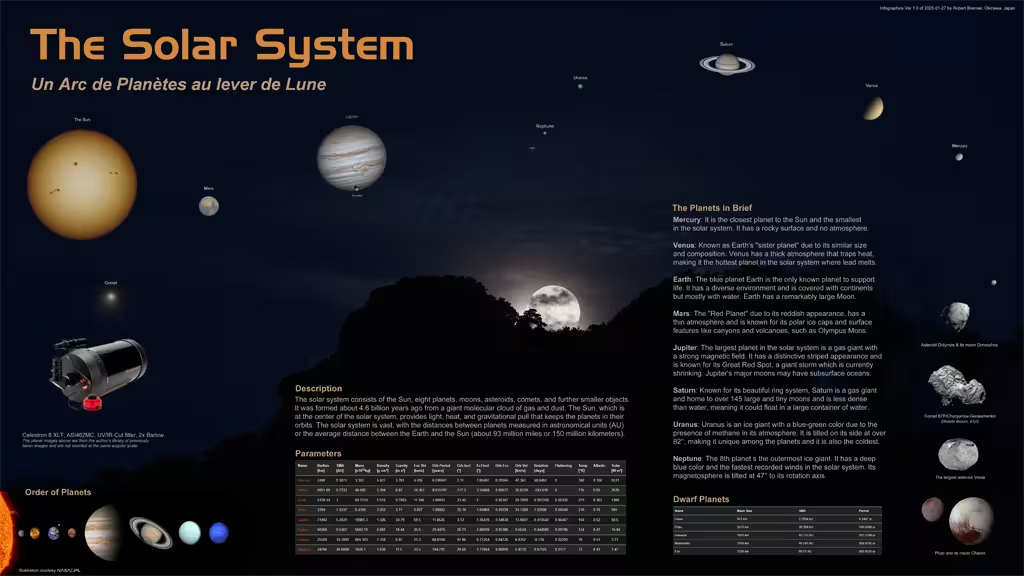
Sun & Moon Today
Observable comet count is 1189
Current exoplanet count is 5885
Current longitude II of the GRS is 72°
Warning: stripos(): Offset not contained in string in /home3/requio/public_html/index.php on line 297
Impact Probablity of 2024 YR4: Insignificant
| Asteroid | Size | Probability | Date |
| 2024 YR4 | 40—90 m | Insignificant | 22 December 2032 |
Please do not let this worry you. The asteroid has been detected just recently meaning that the orbital elements are not yet accurately determined, while they can alter any time due to gravitational pulls.
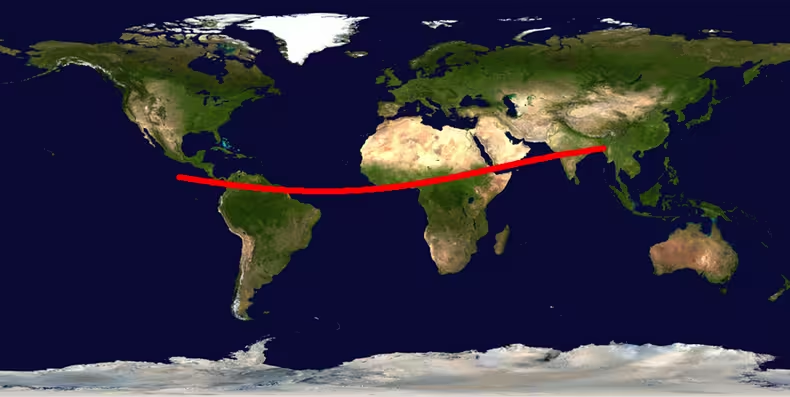
The risk corridor of 2024 YR4's possible impact locations runs from the Pacific Ocean to Northern South America, the Atlantic Ocean, central Africa, a corner of the Arabian peninsula, and then to northern India (Source Wikipedia).
Today Monitor
Planet Oppositions
Mars: January 16, 2025
Jupiter: January 10, 2026
Saturn: September 21, 2025
Uranus: November 21, 2025
Neptune: September 23, 2025
Greatest Elongation of Venus
Evening: January 10, 2025 at 47.2°E
Morning: June 1, 2025 at 45.9°W
Greatest Elongation of Mercury
Morning: December 25, 2024 at 22.0°W
Evening: March 8, 2025 at 18.2°E
Morning: April 21, 2025 at 27.4°W
Evening: July 4, 2025 at 25.9°E
Morning: August 19, 2025 at 18.6°W
Evening: October 29, 2025 at 23.9°E
Morning: December 7, 2025 at 20.7°W
Evening: Febrary 19, 2026 at 18.1°E
Super Moons (full) 2025
Wednesday, 5 November
Friday, 5 December
given for 00:00 UT
In Longitude (negative is western)
| Date | Size | Age | Angle | Phase |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 23 Feb 2025 | 30.61' | 24.48 | -6.502° |  |
| 24 Feb 2025 | 31.06' | 25.48 | -6.683° |  |
| 25 Feb 2025 | 31.54' | 26.48 | -6.463° |  |
| 22 Mar 2025 | 30.16' | 21.97 | -6.602° |  |
| 23 Mar 2025 | 30.54' | 22.97 | -7.220° |  |
| 24 Mar 2025 | 31.00' | 23.97 | -7.497° |  |
| 25 Mar 2025 | 31.50' | 24.97 | -7.380° |  |
| 26 Mar 2025 | 32.03' | 25.97 | -6.841° |  |
| 04 Apr 2025 | 31.86' | 5.54 | 6.674° |  |
| 05 Apr 2025 | 31.40' | 6.54 | 7.159° |  |
| 06 Apr 2025 | 30.97' | 7.54 | 7.233° |  |
| 07 Apr 2025 | 30.58' | 8.54 | 6.935° |  |
| 19 Apr 2025 | 30.14' | 20.54 | -6.609° |  |
| 20 Apr 2025 | 30.49' | 21.54 | -7.247° |  |
| 21 Apr 2025 | 30.91' | 22.54 | -7.602° |  |
| 22 Apr 2025 | 31.38' | 23.54 | -7.618° |  |
| 23 Apr 2025 | 31.89' | 24.54 | -7.248° |  |
| 24 Apr 2025 | 32.39' | 25.54 | -6.459° |  |
| 02 May 2025 | 32.05' | 4.19 | 6.908° |  |
| 03 May 2025 | 31.53' | 5.19 | 7.524° |  |
| 04 May 2025 | 31.04' | 6.19 | 7.652° |  |
| 05 May 2025 | 30.59' | 7.19 | 7.335° |  |
| 06 May 2025 | 30.21' | 8.19 | 6.642° |  |
| 18 May 2025 | 30.56' | 20.19 | -6.624° |  |
| 19 May 2025 | 30.92' | 21.19 | -6.950° |  |
| 20 May 2025 | 31.32' | 22.19 | -7.010° |  |
| 21 May 2025 | 31.75' | 23.19 | -6.758° |  |
| 30 May 2025 | 32.13' | 2.87 | 6.436° |  |
| 31 May 2025 | 31.63' | 3.87 | 7.137° |  |
| 01 Jun 2025 | 31.12' | 4.87 | 7.336° |  |
| 02 Jun 2025 | 30.65' | 5.87 | 7.064° |  |
| 29 Jun 2025 | 31.11' | 3.56 | 6.528° |  |
| 02 Oct 2025 | 30.80' | 10.17 | -6.602° |  |
| 03 Oct 2025 | 31.28' | 11.17 | -6.712° |  |
| 04 Oct 2025 | 31.79' | 12.17 | -6.413° |  |
| 13 Oct 2025 | 32.01' | 21.17 | 6.426° |  |
| 14 Oct 2025 | 31.60' | 22.17 | 7.017° |  |
| 15 Oct 2025 | 31.20' | 23.17 | 7.219° |  |
| 16 Oct 2025 | 30.83' | 24.17 | 7.068° |  |
| 17 Oct 2025 | 30.51' | 25.17 | 6.617° |  |
| 29 Oct 2025 | 30.28' | 7.48 | -6.622° |  |
| 30 Oct 2025 | 30.70' | 8.48 | -7.213° |  |
| 31 Oct 2025 | 31.18' | 9.48 | -7.461° |  |
| 01 Nov 2025 | 31.71' | 10.48 | -7.298° |  |
| 02 Nov 2025 | 32.24' | 11.48 | -6.672° |  |
| 10 Nov 2025 | 32.23' | 19.48 | 7.097° |  |
| 11 Nov 2025 | 31.72' | 20.48 | 7.804° |  |
| 12 Nov 2025 | 31.23' | 21.48 | 8.024° |  |
| 13 Nov 2025 | 30.78' | 22.48 | 7.808° |  |
| 14 Nov 2025 | 30.39' | 23.48 | 7.230° |  |
| 26 Nov 2025 | 30.27' | 5.72 | -6.459° |  |
| 27 Nov 2025 | 30.63' | 6.72 | -7.095° |  |
| 28 Nov 2025 | 31.05' | 7.72 | -7.447° |  |
| 29 Nov 2025 | 31.52' | 8.72 | -7.439° |  |
| 30 Nov 2025 | 32.02' | 9.72 | -7.008° |  |
| 08 Dec 2025 | 32.44' | 17.72 | 6.680° |  |
| 09 Dec 2025 | 31.91' | 18.72 | 7.561° |  |
| 10 Dec 2025 | 31.38' | 19.72 | 7.916° |  |
| 11 Dec 2025 | 30.87' | 20.72 | 7.788° |  |
| 12 Dec 2025 | 30.43' | 21.72 | 7.247° |  |
| 26 Dec 2025 | 31.06' | 5.93 | -6.615° |  |
| 27 Dec 2025 | 31.43' | 6.93 | -6.624° |  |
In Latitude (negative is southern)
| Date | Size | Age | Angle | Phase |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12 Jan 2025 | 31.85' | 12.07 | -6.565° |  |
| 13 Jan 2025 | 31.60' | 13.07 | -6.448° |  |
| 26 Jan 2025 | 30.57' | 26.07 | 6.621° |  |
| 27 Jan 2025 | 30.96' | 27.07 | 6.622° |  |
| 08 Feb 2025 | 31.60' | 9.48 | -6.682° |  |
| 09 Feb 2025 | 31.36' | 10.48 | -6.624° |  |
| 22 Feb 2025 | 30.21' | 23.48 | 6.703° |  |
| 23 Feb 2025 | 30.61' | 24.48 | 6.800° |  |
| 24 Feb 2025 | 31.06' | 25.48 | 6.559° |  |
| 07 Mar 2025 | 31.74' | 6.97 | -6.762° |  |
| 08 Mar 2025 | 31.39' | 7.97 | -6.766° |  |
| 09 Mar 2025 | 31.05' | 8.97 | -6.404° |  |
| 21 Mar 2025 | 29.85' | 20.97 | 6.665° |  |
| 22 Mar 2025 | 30.16' | 21.97 | 6.852° |  |
| 23 Mar 2025 | 30.54' | 22.97 | 6.721° |  |
| 03 Apr 2025 | 32.33' | 4.54 | -6.682° |  |
| 04 Apr 2025 | 31.86' | 5.54 | -6.784° |  |
| 05 Apr 2025 | 31.40' | 6.54 | -6.493° |  |
| 17 Apr 2025 | 29.65' | 18.54 | 6.506° |  |
| 18 Apr 2025 | 29.86' | 19.54 | 6.754° |  |
| 19 Apr 2025 | 30.14' | 20.54 | 6.698° |  |
| 30 Apr 2025 | 32.98' | 2.19 | -6.438° |  |
| 01 May 2025 | 32.55' | 3.19 | -6.675° |  |
| 02 May 2025 | 32.05' | 4.19 | -6.485° |  |
| 15 May 2025 | 29.78' | 17.19 | 6.605° |  |
| 16 May 2025 | 29.99' | 18.19 | 6.587° |  |
| 28 May 2025 | 32.97' | 0.87 | -6.528° |  |
| 29 May 2025 | 32.60' | 1.87 | -6.460° |  |
| 11 Jun 2025 | 29.82' | 14.87 | 6.526° |  |
| 12 Jun 2025 | 30.02' | 15.87 | 6.530° |  |
| 24 Jun 2025 | 32.85' | 27.87 | -6.457° |  |
| 25 Jun 2025 | 32.68' | 28.87 | -6.502° |  |
| 08 Jul 2025 | 29.84' | 12.56 | 6.561° |  |
| 09 Jul 2025 | 30.07' | 13.56 | 6.600° |  |
| 21 Jul 2025 | 32.45' | 25.56 | -6.493° |  |
| 22 Jul 2025 | 32.38' | 26.56 | -6.624° |  |
| 04 Aug 2025 | 29.76' | 10.20 | 6.646° |  |
| 05 Aug 2025 | 29.99' | 11.20 | 6.748° |  |
| 06 Aug 2025 | 30.28' | 12.20 | 6.541° |  |
| 17 Aug 2025 | 32.23' | 23.20 | -6.553° |  |
| 18 Aug 2025 | 32.11' | 24.20 | -6.755° |  |
| 19 Aug 2025 | 31.94' | 25.20 | -6.550° |  |
| 31 Aug 2025 | 29.61' | 7.75 | 6.661° |  |
| 01 Sep 2025 | 29.78' | 8.75 | 6.848° |  |
| 02 Sep 2025 | 30.05' | 9.75 | 6.733° |  |
| 13 Sep 2025 | 32.46' | 20.75 | -6.508° |  |
| 14 Sep 2025 | 32.22' | 21.75 | -6.794° |  |
| 15 Sep 2025 | 31.95' | 22.75 | -6.665° |  |
| 27 Sep 2025 | 29.47' | 5.17 | 6.540° |  |
| 28 Sep 2025 | 29.56' | 6.17 | 6.805° |  |
| 29 Sep 2025 | 29.74' | 7.17 | 6.779° |  |
| 30 Sep 2025 | 30.01' | 8.17 | 6.453° |  |
| 11 Oct 2025 | 32.77' | 19.17 | -6.687° |  |
| 12 Oct 2025 | 32.41' | 20.17 | -6.652° |  |
| 25 Oct 2025 | 29.42' | 3.48 | 6.651° |  |
| 26 Oct 2025 | 29.52' | 4.48 | 6.681° |  |
| 27 Oct 2025 | 29.69' | 5.48 | 6.423° |  |
| 07 Nov 2025 | 33.37' | 16.48 | -6.472° |  |
| 08 Nov 2025 | 33.10' | 17.48 | -6.565° |  |
| 21 Nov 2025 | 29.39' | 0.72 | 6.513° |  |
| 22 Nov 2025 | 29.46' | 1.72 | 6.567° |  |
| 05 Dec 2025 | 33.44' | 14.72 | -6.511° |  |
| 18 Dec 2025 | 29.42' | 27.72 | 6.502° |  |
| 19 Dec 2025 | 29.48' | 28.72 | 6.570° |  |
Source: NASA/GSFC
Latest STScI News Release
Eye on Infinity: NASA Celebrates Hubble's 35th Year in Orbit

April 23, 2025
Composite shows portions of four Hubble images from left to right. First, the left half of Mars in shades of orange, blues, and browns. Second, a tiny portion of the Rosette Nebula shows very dark gray material against a translucent blue background. Third, a portion of planetary nebula NGC 2899 looks like the number three in shades of red and orange. Fourth, the center of barred spiral galaxy NGC 5335 has a milky yellow center that forms a bar surrounded by the beginnings of blue star-filled spiral arms.
Source: stsci.edu/news
Latest JWST News
Webb uncovers possible hidden supermassive black hole in nearby spiral galaxy M83

17 April 2025
Astronomers using the NASA/ESA/CSA James Webb Space Telescope have discovered evidence that suggests the presence of a long-sought supermassive black hole at the heart of the nearby spiral galaxy Messier 83 (M83). This surprising finding, made possible by Webb’s Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI), reveals highly ionised neon gas that could be a telltale signature of an active galactic nucleus (AGN), a growing black hole at the center of a galaxy.
Source: esawebb.org
JWST Picture of the Month
Infrared, optical, and X-ray views of a galaxy group

29 April 2025
This new Picture of the Month from the NASA/ESA/CSA James Webb Space Telescope features an astounding number of galaxies. The objects in this frame span an incredible range of distances, from stars within our own Milky Way, marked by diffraction spikes, to galaxies billions of light-years away. The star of this field is a group of galaxies, the largest concentration of which can be found just below the centre of this image. These galaxies glow with white-gold light. We see this galaxy group as it appeared when the Universe was 6.5 billion years old, a little less than half the Universe’s current age. The image on the left combines infrared data from both Webb and the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope, showcasing the galaxy cluster against a backdrop of thousands of other galaxies. The image on the right adds X-ray data from ESA’s XMM-Newton space observatory and NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory …
Source: esawebb.org
NASA Image of the Day
Back to Earth
The Soyuz MS-26 spacecraft is pictured backing away from the International Space Station shortly after undocking from the Rassvet module on April 19, 2025. The Soyuz crew ship would parachute to a landing in Kazakhstan about three hours later returning NASA astronaut Don Pettit and Roscosmos cosmonauts Alexey Ovchinin and Ivan Vagner back to Earth after a 220-day space research mission.
Click to enlarge or show full screenFri, 02 May 2025 18:32 GMT
Source: www.nasa.gov
Life on Exoplanet K2-18b?

Image credit: Grok (modified with red star)
2025-04-18 Exoplanets
Thanks to NASA's JWST, astronomers have detected signatures of life on the exoplanet K2-18b, 124 light-years away in Leo, which is 2.6 times larger and 8.6 times more massive than the Earth. The planet's atmosphere contains dimethyl sulfide (DMS), naturally produced by living organisms. Already in September 2023 NASA reported that the JWST has revealed the presence of carbon-bearing molecules including methane and carbon dioxide. Link to source 🔗
Direct Images of Gas Giant Planets

Image credit: NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, W. Balmer (JHU), L. Pueyo (STScI), M. Perrin (STScI)
2025-03-18 Exoplanets
HR 8799 is a young star with 1.5 solar masses, about 130 light-years away in Pegasus and known to have four giant gas planets rich in carbon dioxide gas. NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope took a spectrum and imaged the four planets while the light of the star has been blocked. Link to source 🔗
Barnard's Four Tiny Planets

Image credit: International Gemini Observatory/NOIRLab/NSF/AURA/R. Proctor/J. Pollard
2025-03-14 Exoplanets
Next to the Alpha Centauri system, Barnard's star is the second nearest at 5.96 light-years away in Ophiuchus. As of March 2025, the red dwarf star, only 0.16 as massive as the sun, is home to four known (confirmed) planets each of them less than half the mass of Earth and none of them orbiting inside the habitable zone. Only between 2.8 and 4.1 million kilometers away from the star on 2.34 to 6.74 days orbits, their surfaces are supposed to be heat scorched with no outlook for life. Link to source 🔗
Asteroid 2024 YR4

Image credit: European Space Agency
2025-02-07 solar system
2024 YR4 is an extremely faint asteroid with a low albedo of 5% to 25% and is 40 to 90 meters in size which, as of today, has a minute 2.2% probability of impacting Earth at 14:02 UTC on December 22, 2032. The asteroid rotates around its axis every 19.5 minutes and travels around the sun on a highly 0.662 eccentric orbit plane once in about 4 years at a mean distance of 2.5165 AU. Its last perihelion (sun passage) occurred on 2024-Nov-22. The iron-nickel asteroid that created the Barringer Crater in Arizona 50,000 years ago was about 50 meters wide. Link to source 🔗
Nearby Venus-Like Planet
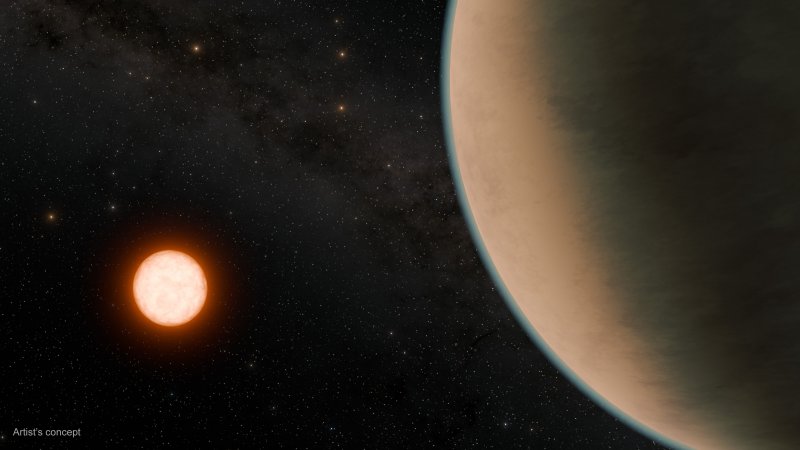

Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/R. Hurt (Caltech-IPAC)
2025-02-01 Exoplanets
Gliese 12 (TOI-6251) is a red dwarf star some 40 light-years away in Pisces. Its known planet, b, about the same size as Venus and, because a red dwarf is much cooler than our sun, the planet also receives the same amount of energy from its host star although orbiting much closer and once in about 12.8 days. In astronomical terms, the planet lies nearby and is a potentially terrestrial, temperate exoplanet inviting further investigations, such as atmospheric spectroscopy with the help of the JWST. Link to source 🔗
New Space Telescope SPHEREx
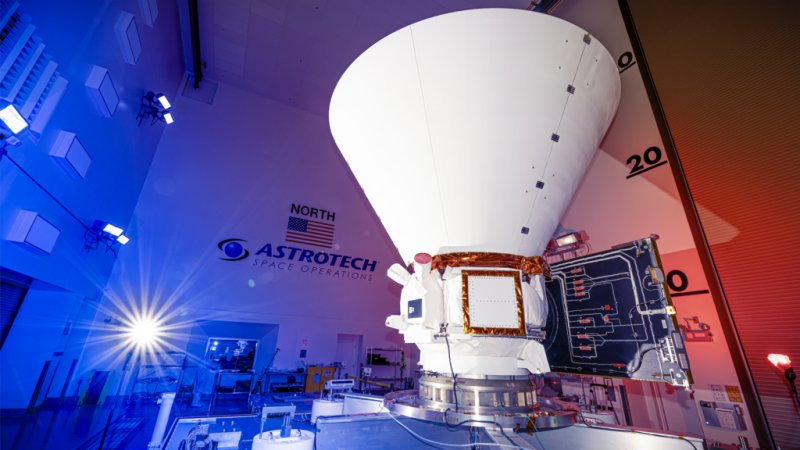

Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
2025-01-31 Universe
Scheduled for launch past February 2025, SPHEREx is NASA's latest orbiting space telescope, designed for a spectral survey of the entire sky for a duration of tentatively two years in order to explore the origins of the universe. Link to source 🔗
Blackhole Binary
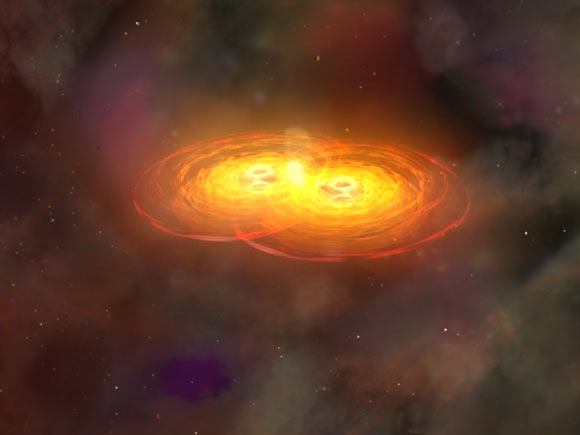

Image credit: NASA / CXC / A. Hobart / Josh Barnes, University of Hawaii / John Hibbard, NRAO
2025-01-20 galaxies
Astronomers at the University of Tokyo discovered a rare quasar-like object with a long-term periodic luminosity variation with a cycle of about 190 days. Two black holes moving periodically at high speed may be the cause of the variability, hypothetically a supermassive blackhole binary. The extremely luminous object lies in the constellation of Hydra and is designated J0909+0002 in short. Link to source 🔗
A new Type of Planet?
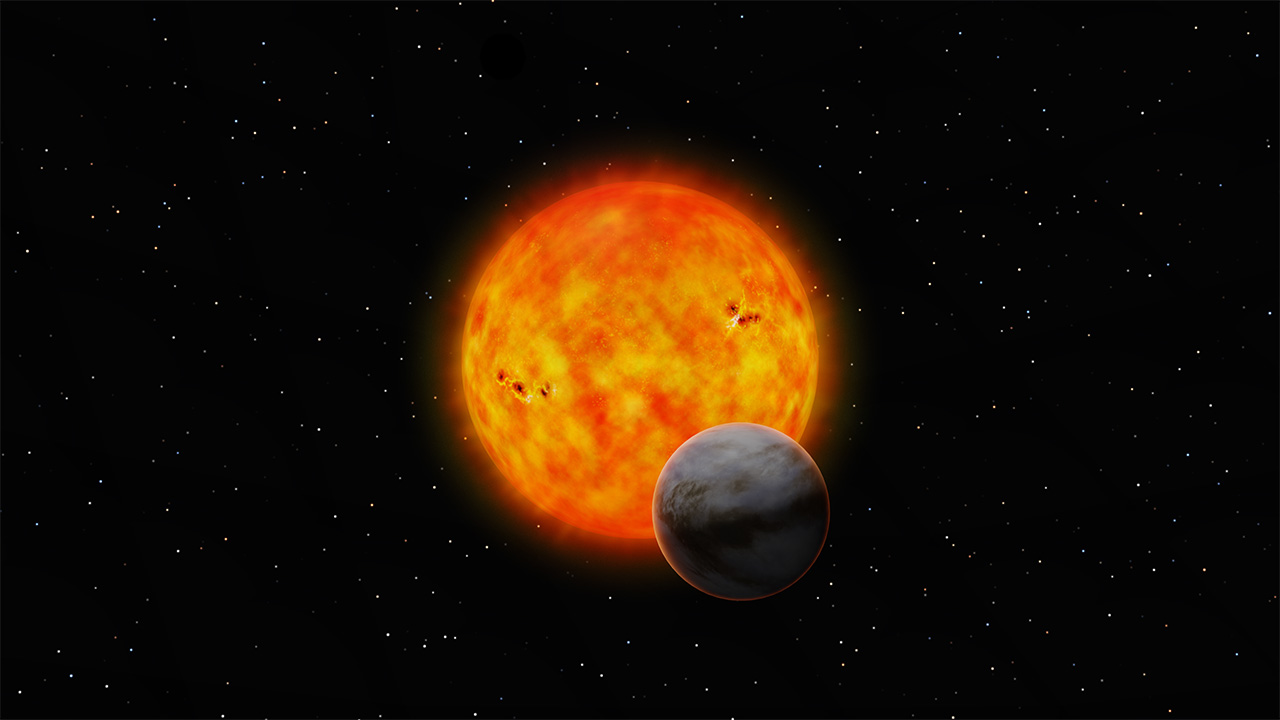

Image credit: NAOJ
2025-01-15 Exoplanets
Using the James Webb Space Telescope, astronomers scanned the atmosphere of the planet GJ1214 b located 48 light-years away in Ophiuchus. Instead of a hydrogen rich super-Earth, or a water world, the new data, in spite of many uncertainties, revealed concentrations of carbon-dioxide (CO2) comparable to the levels found in the dense CO2 atmosphere of Venus. Link to source 🔗
Backlog
No, we are not on Facebook but proudly on AstroBin with Mille Gracie to the author Salvatore Iovene:

GoTo Astropical on AstroBin
If anybody is interested in the night life of bats, here is a funny 1-minute MP4 video (24MB).
Recent
1. Certain people appear to enjoy filling forms with random letters for no purpose but insane self-satisfaction. Most of this stupid folks leave their IP addresses which are forwarded to their provider companies. All so received forms are automatically deleted. Sadly, the world is overfilled with idiots, trolls and criminals. This is a public web site without any sensitive data. No need for these irrational displays.
2. Now in the process of changing all large images to AVIF or WEBP format resulting in considerably reduced file size and download time hardly sacrificing quality as compared with JPEG.
Legal
In case of abuse or hacking attempts, we reserve the right to report to providers, ISPs and legal authorities. The contents of this site is public, no hidden secrets. The data is backed up in regular intervals.
Cookies
This website does NOT send and use "cookies".
Privacy
Your visit is anonymous. The author processes merely the data that a web browser is typically sending back. The only purpose is for the [Visitors Online] section below.
Free Registration
In order for location dependent data to show correctly you need to register. In the interest of your privacy this website does not automatically retrieve your location via third party services, etc.
Compatibility
Website tested under Windows and Android only. Although largely compatible with smartphones this website is primarily designed for desktops, note books and tablets. This applies in particular to database tables. Double click on page top banners to remove them.
Monitor Calibration
Please adjust your monitor's gamma and contrast, etc. if you cannot distinguish all shades of gray. Click for an enlarged color pattern.
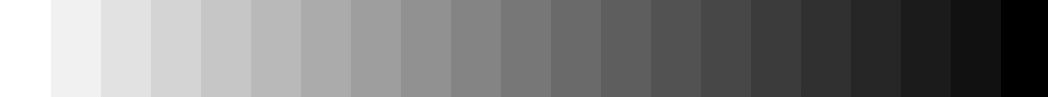
URL Request
If you do not wish to register (no problem) but need to see data for your location only once or so, then you can add the following string to the URL:
?lat=xx.xxx&lon=xxx.xxx&tzn=z.zz
where xx.xxx need to be replaced by your geographic coordinates, z.zz with your time zone. This data will not be stored.
This 'once-view' will work for most pages, such as Planisphere, Deepsky Observer, Ephemerides and Today Monitor.
 US, Wisconsin, Saint Francis
US, Wisconsin, Saint FrancisLast visit from: US

on page apscopes.php using Windows O/S.
Unique visitors today: 73 (since 0:00 UTC) from:



















Newest flag:  -- Welcome!
-- Welcome!
Total page views 534 since 2025-05-01
from 40 different countries (excluding bots & idiots).







































Operating SystemsWindows: 170iPhone: 137 Macintosh: 123 Linux: 42 Android: 38 Unknown: 12 Other: 10 iPad: 2 |
Most Visitedindex.php: 188apscopes.php: 42 algol.php: 35 crafts.php: 28 nikond5300.php: 23 swsamount.php: 16 recons.php: 13 fovslider.php: 11 exoplnt.php: 10 solsyst.php: 8 |
Site Updates
- 2025-03-30 • Astro Weather added (middle column)
- 2025-03-29 • Article reviewed & updated.
- 2025-02-23 • Exoplanet single page fixed.
- 2025-02-17 • ISS Live Cameras fixed.
- 2025-02-17 • Orion Atlas EQ-G Hints added
- 2025-02-16 • EG6-R Pro Mount Review added
- 2025-02-07 • Mounts for AP added
- 2025-01-25 • New Deepsky Poster added
- 2025-01-25 • Lunar Posters added
- 2025-01-20 • Mini Posters added
- 2025-01-02 • Planet ephemerides updated
- 2025-01-01 • Libration calendar updated
- 2024-10-07 • Various minor changes and code fixes
- 2024-10-07 • Aladin removed as not own work
- 2024-05-14 • JWST Images added to Top Page
- 2024-01-09 • Exoplanets with PHL/HWC
- 2023-12-27 • Tomytec Borg telescopes added.
- 2023-12-23 • Takahashi telescopes added.
- 2023-12-21 • Asteroid Dinkinesh & Didymos added.
- 2023-12-18 • Telescopes for AP updated
- 2023-12-02 • Libration calendar 2024 uploaded
- 2023-12-01 • Ephemeris updated for 2024
- 2023-11-16 • Libration data for 2024 updated
- 2023-11-14 • Review BKP150 updated
- 2023-11-13 • Review TS71SDQ updated
- 2023-09-18 • Page Optical Train added
- 2023-10-21 • New PDF brochure added
- 2023-09-18 • Review: Uranus-C added
- 2023-01-21 • EAA for Starters PDF added

Deepsky Overview
My Humble Gallery
Lunar Imaging
FOV Simulator
Astro Cameras

Let's Astrophoto
Telescopes for AP
Total Exoplanet Count: 5885
Kepler/K2: 3328 planetsTESS: 620 planets
Latest exoplanet around:
as of 2025-04-21
| Constellation | Pegasus |
| Distance | 535.69 parsec |
| Magnitude | 12.67 vis. |
| Mass | 1.08 xSun |
| Radius | 1.375 xSun |
| Temperature | 5990°K |
| Known planet(s) | 1 |
Acton Sky Portal Observatory 2
Anglo-Australian Telescope 35
Apache Point Observatory 2
Arecibo Observatory 3
Atacama Large Millimeter Array (ALMA) 1
Bohyunsan Optical Astronomical Observatory 26
Calar Alto Observatory 26
Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory 5
CHaracterising ExOPlanets Satellite (CHEOPS) 3
CoRoT 35
European Southern Observatory 3
European Space Agency (ESA) Gaia Satellite 13
Fred Lawrence Whipple Observatory 6
Gemini Observatory 13
Haleakala Observatory 2
HATNet 67
HATSouth 73
Haute-Provence Observatory 67
Hubble Space Telescope 6
Infrared Survey Facility 1
James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) 1
K2 547
KELT 10
KELT-North 7
KELT-South 4
Kepler 2781
Kitt Peak National Observatory 1
KMTNet 103
KOINet 1
La Silla Observatory 286
Large Binocular Telescope Observatory 3
Las Campanas Observatory 29
Leoncito Astronomical Complex 1
Lick Observatory 36
Lowell Observatory 3
Mauna Kea Observatory 3
McDonald Observatory 31
MEarth Project 2
MOA 31
Multiple Facilities 18
Multiple Observatories 325
NASA Infrared Telescope Facility (IRTF) 1
Next-Generation Transit Survey (NGTS) 21
OGLE 106
Okayama Astrophysical Observatory 36
Palomar Observatory 2
Paranal Observatory 30
Parkes Observatory 2
Qatar 10
Roque de los Muchachos Observatory 35
South African Radio Astronomy Observatory (SAR 1
SPECULOOS Southern Observatory 2
Spitzer Space Telescope 4
Subaru Telescope 11
SuperWASP 122
SuperWASP-North 5
SuperWASP-South 32
Teide Observatory 1
Thueringer Landessternwarte Tautenburg 8
Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) 620
TrES 5
United Kingdom Infrared Telescope 2
University of Canterbury Mt John Observatory 1
Very Long Baseline Array 1
W. M. Keck Observatory 189
WASP-South 11
Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer (WISE) Sat 1
Winer Observatory 1
Xinglong Station 2
XO 6
Yunnan Astronomical Observatory 3
Zwicky Transient Facility 2
Next NEO Approach
2024 JM2 on 2025-May-03 09:33 UTC at 7.1414 LD
Random Objects
Polaris Australis (Sig Ser) in Ser [HIP 104382]
Distance: 270 light-years, Magnitude: 5.45
Sigma Octantis is also called 'Polaris Australis' for being the South Star and represents the State of Distrito Federal on the flag of Brazil. To an observer in the southern hemisphere, Sigma Octantis appears almost motionless and all the other stars in the Southern sky appear to rotate around it. It is part of a small "half hexagon" shape. It is over a degree away from the true south pole, and the south celestial pole is moving away from it due to precession of the equinoxes. The star is too dim for navigational purposes.
Star Chart | DSS IR Image 🔗GJ 166 C (40 Eridani C) in Eridanus
Distance: 16 light-years, Magnitude: 11.2
40 Eridani C is a 11th magnitude red dwarf flare star, a variable designated DY Eridani.
Star Chart | DSS IR Image 🔗

M97 (Planetary Nebula) in Ursa Major
Magnitude: 12
M97 is a very unusual and dynamic planetary nebula spanning 3 light-years. Inside a 6,000 years old shell is a dying 16th magnitude star 0.7x the mass of our Sun.
Star Chart | DSS IR Image 🔗Columba (southern), area rank: 54
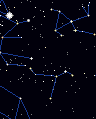
Located southwest of Canis Major, this constellation depicts the shape of the letter T formed by 3rd-magnitude stars. Modelled after the dove in the Old Testimony, the constellation picture draws a dove holding a branch in its mouth.
Star Chart246P/NEAT

246P/NEAT is a periodic comet discovered on 2004 March 28 by Near-Earth Asteroid Tracking (NEAT) using the 1.2-meter reflector at Haleakala. It was given the permanent number 246P on 2011 January 14. It is a Quasi-Hilda comet. Due to perturbations by Jupiter, the 2005, 2013 and 2021 perihelion passages will be closer to the Sun. The comet is observable all through its orbit. [Wikipedia]
Lachesis (Asteroid)
Semi-major: 3.11489 AU, Size: 175 km

Discovered by French astronomer Alphonse Borrelly on April 10, 1872, and independently by German-American astronomer Christian Heinrich Friedrich Peters on April 11, 1872, Lachesis is a C-type main belt asteroid it is probably composed of carbonaceous material. Lachesis has a axial rotation period of 46.551 hours with a brightness variation of 0.14 in magnitude. The asteroid has a mean mass of 5.5x1018kg.
S/2004 N1 (moon of Neptune)

Mark Showalter of the SETI Institute in Mountain View, Calif., found the moon July 1, 2013 while studying the segments of rings around Neptune in more than 150 archival Neptune photographs taken by Hubble from 2004 to 2009. Designated S/2004 N1, this smallest known moon of Neptune is no more than 20 km wide and so faint that it has been overlooked for many years although the Hubble images were in the public domain. S/2004 N1 appears to be traveling in a near-circular orbit very close to Neptune's equatorial plane.
HD 180617 b (in Aquila)
Mass: 0.0384293 xJup
SMA: 0.343 AU
Period: 105.911 days
Distance: 5.91059 parsec
Category: Warm Neptunian
ESI: 0.44
Android Astronomy Apps
3D Visualizations
Solar System
Planets
Mercury | Venus | Venus Radar | Earth | Earth Melted | Earth Cretaceous | Mars | Mars Terraformed | Jupiter | Saturn | Uranus | Neptune | Planet Nine (hypothetical)Dwarf Planets
Ceres | Pluto | Haumea | Makemake | Eris | KBOAsteroids
Vesta | Pallas (fictive) | Juno (fictive) |Planetary Moons
Ariel (Uranus) | Callisto (Jupiter) | Charon (Pluto) | Dione (Saturn) | Enceladus (Saturn) | Europa (Jupiter) | Ganymede (Jupiter) | Iapetus (Saturn) | Io (Jupiter) | Mimas (Saturn) | Miranda (Uranus) | Moon (Earth) | Oberon (Uranus) | Rhea (Saturn) | Tethys (Saturn) | Titan (Saturn) | Titania (Uranus) | Triton (Neptune) | Umbriel (Uranus)Comets
67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko (takes a minute to download)Exoplanets
Exoplanets
Rocky Terran | Ocean Terran | Hot Terran | Warm Terran | Desert Terran | Water Terran | Second Earth | Cloud Planet | Jovian Planet | Saturnian PlanetEarth
Beautiful Earth
Earth in hi-res (can take a minute to download)Earth at Night
Panoramic view (can take a minute to download)